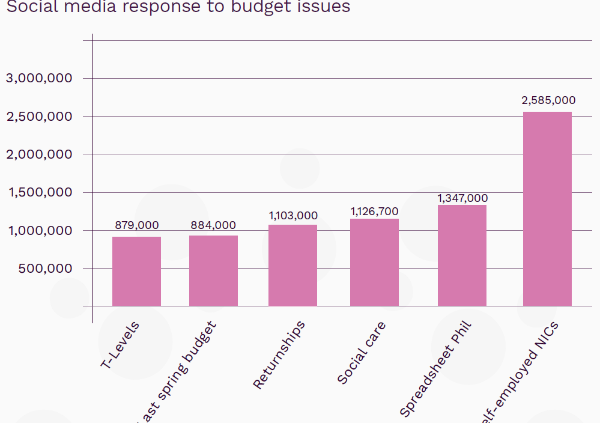
Donald Trump appeared calm and measured during his victory speech, but many are nervous and anxious about a man who will soon become the 45th President of America. With his ten-year-old son by his side and Mike Pence, the new vice president on his right, Trump, despite running a divisive campaign, promised to be a president for ‘all Americans’. Having made countless racist, misogynistic, Islamophobic, and homophobic comments, many are sceptical about Trump’s ability to unite a country that is hugely divided.
Trump’s victory will also signal a new era for international relations. Since this morning there has been turbulence in the global stock markets with a fall in the value of the US dollar. Although Trump does not take office until January he has already had an enormous impact on international relations. To evaluate this high-profile communications professionals and bloggers have spoken to us about their reactions to the US election results and what they think future holds.
Rev. Stuart Campbell: Blogger, Wings Over Scotland

“My reaction to the result is horror, and a total lack of surprise. I’ve been predicting constantly since last November that if it came to a contest between Trump and Clinton, Trump would win it, and so it proved. He won because this election wasn’t about voting for a President, it was about voting against one. They were the least popular candidates in history, and at least half the electorate was voting for them only because they thought the other one was worse.
“In that contest, Clinton was by a country mile the worst nominee the Democrats could possibly have put forward. In fact, you couldn’t have designed someone more perfect from Trump’s perspective. He sold himself as the anti-establishment figure – however absurd it is for a billionaire businessman to do that – and Clinton is the absolute ultimate stereotype of a dynastic insider.
“She’s unconvincing as a human being – smug, robotic and patronising – and mired in all sorts of controversy. She makes more money for giving a 60-minute speech to some bankers than most voters can earn in a decade. Who could ever identify with her?
“Her nomination reeked of Buggins’ turn more than any sort of merit. Pretty much any other candidate would have beaten Trump handily, but none of his litany of monstrous traits made Clinton any more likeable, and her campaign was woeful. Much like the Remain campaign in the EU referendum, if she’d simply stayed at home and left the stage to Trump she’d probably have won, but the very sight of her put people’s backs up.
“The Democrats have gotten exactly what they deserved. Whether America has or not remains to be seen.”
Sarah Pinch: Chart.PR FCIPR MIoD

“My reaction to Donald Trump winning the US presidential election was disappointment. Regardless of my personal support, I’m a woman, a working mother and Trump’s policies and rhetoric do not appeal to me in any way. He has made a case all through his campaign to try to undermine women and girls; he’s undermined non-white Americans, and his campaigning was littered with messages of difference and intolerance.
“But in every moment like this there is hope. Hope that women and men who are sleeping activists wake up and take action. We have a responsibility to redress the balance.
“I’m very disappointed that we have still not heard from Hillary Clinton. She needs to stand up and face the music, with dignity quickly.”
“Donald Trump is a media man. In some ways, that may be a good thing. His campaign was successful, so we need to look and understand why. But we must guard against further polarisation of our society. We have a key time as professional communicators to ensure balance, fairness and ethical engagement.”
James Dowling: Head of Public Policy, Lansons

“I believe that Donald Trump winning the election simply increases the level of uncertainty we are seeing. Trump is untested in any elected office, and has proved through this campaign that he does not play by the normal rule book. He will say what he thinks and do what he wants – and has succeeded despite this. This calls into question the role of the US President and the global order. For example, how will he deal with Russia – both in Syria and in Europe. His relationship with Vladimir Putin has been called into question throughout the campaign, so there is a clear sense of uncertainty around whether Russia will feel empowered to push the boundaries further, and how Trump will respond if that happens. He has also said he would ‘dismantle’ the nuclear deal with Iran – a deal that was only agreed in 2015, after years of negotiation. On global trade, Trump has vowed to scrap the ‘TTIP’ deal with the EU and the Trans Pacific Partnership. He will also rewrite the North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement.
“However, Trump’s election also brings opportunity. The capture of congress by the Republicans gives the US an opportunity to pass real and life changing legislation. Americans have been sick of the gridlock that has occurred in Government and may see this as an opportunity. If he can work with Capitol Hill, President Trump will enjoy huge power to deliver on a number of areas. He has promised corporation tax reform – this may now be possible. For the UK, Trump has cited Brexit as an inspiration and promised a free trade deal. Despite the wider uncertainties, this may well help the UK as it pivots from Europe to the wider world.
“In relation to the global impact the new president will have on the comms industry, I think it simply adds to the uncertainty we are seeing. Comms professionals are able to help their clients understand how to react – and to deal with their key audiences. Some of the lessons we are learning from Brexit are relevant here too.
“The firms that will profit are those that best understand the nature of the challenge, and can respond accordingly. For businesses exporting to or highly dependent on the US market, the comms world can help clients speak to those who can help them push or manage their concerns in the UK and the US – whether with Government, regulators or investors. Domestically, there is a risk that this feeds a wider sense of uncertainty which could translate to further caution in consumer spending. Consumer-facing organisations will need help to respond – communications professionals are best-placed to help them do so.”
Sarah Hall: founder and editor of #FuturePRoof, and CIPR President-Elect 2017

“Trump’s victory goes to show we truly are living in a post-fact era. His success underlines what happens when politicians appeal to the emotions regardless of whether what they are saying is true.
“Despite communicating the potentially catastrophic consequences of having someone unqualified and inexperienced at the helm, Clinton’s campaign was not strong enough to fight underlying anxieties about terrorism and national security, which Trump fed with passionate rhetoric.
“The FBI’s unprecedented intervention a week before voting seriously damaged Clinton’s campaign, creating further trust issues, and no amount of celebrity advocacy was able to disguise her unpopularity with many.
“The fact that in a reality show obsessed society, a TV reality star has been elected as the President of America must also be seen as a contributing factor, creating cut through and a sense of commonality for Trump with the masses.”